东北地理所在饲用抗生素降低“秸秆养牛-粪便基质发酵-草生菌栽培”循环系统中氮转化的作用机理研究方面取得进展
氮参与蛋白质、核酸等生命必需生物大分子的合成,是生物体中至关重要的成分。生物圈中的氮循环是氮的生物地球化学循环的重要组成部分之一。随着农业和畜牧业的发展,大量畜禽粪便和农作物秸秆被闲置、浪费,并被称为“农业废弃物”。种养循环技术模式是促进营养物质循环利用、提高农牧业生产效率的重要农业生产方式。然而,到目前为止,种养循环系统中关于氮循环效率及其调控的研究还非常薄弱。为此,中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所草地农牧业学科组的科研人员基于“玉米秸秆养牛-粪便基质化-草生菌栽培”循环系统,研究了莫能菌素及秸秆种类对氮回收率的影响(氮回收率定义为蘑菇子实体中总氮与初始原料中总氮的比值),旨在明确该循环系统中氮的回收率,并揭示莫能菌素影响循环系统中氮转化的微生物学机制。
研究发现:在4种发酵基质(无抗牛粪+玉米秸秆、无抗牛粪+小麦秸秆、有抗牛粪+玉米秸秆、有抗牛粪+小麦秸秆)上栽培双孢蘑菇,可以蘑菇氮的形式回收秸秆和粪便中总氮的3.33-5.88%。由于残留的莫能菌素抑制了基质中氨化与反硝化菌的活性,从而降低了基质发酵过程中的氮损失,提高了氮转化效率(表1)。然而,由于发酵和栽培过程中,基质中与氮转化相关的酶活性(表2)以及微生物群落结构和演替变化(图1)引起的氮损失变化,莫能菌素最终降低了整个循环系统中氮回收率的0.13%-1.57%。本研究结果为构建高效的种养一体化循环农业技术模式提供了数据支撑。
表1. 基质发酵、蘑菇栽培及采收过程中的氮回收率
|
Stages |
Items |
Treatment1 |
SEM |
Pvalue | |||||
|
No-antibiotic |
Antibiotic | ||||||||
|
NC |
NW |
AC |
AW |
Straw |
Antibiotic |
Straw×Antibiotic | |||
|
Start of fermentation |
Starting substrate (kg) |
15.12 |
15.22 |
15.18 |
15.21 |
0.042 |
0.129 |
0.650 |
0.378 |
|
N concentration in starting substrate (g/kg) |
16.45c |
18.96a |
16.21d |
18.73b |
0.035 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
0.981 | |
|
Total N in starting substrate (g) |
248.7c |
288.7a |
246.1d |
284.8b |
0.855 |
<0.001 |
0.001 |
0.462 | |
|
End of fermentation |
Fermented substrate (kg) |
11.20b |
10.65c |
11.41c |
10.38d |
0.035 |
<0.001 |
0.342 |
<0.001 |
|
N concentration in fermented substrate (g/kg) |
21.08b |
21.54b |
21.01b |
22.87a |
0.299 |
<0.001 |
0.047 |
0.029 | |
|
Total N in fermented substrate (g) |
236.1 |
229.4 |
239.6 |
237.3 |
3.316 |
0.189 |
0.098 |
0.516 | |
|
N retention rate during fermentation2(%) |
94.93a |
79.45c |
97.37a |
83.33b |
1.194 |
<0.001 |
0.016 |
0.555 | |
|
End of cultivation |
Cultivated substrate (kg) |
6.96b |
7.14a |
6.81c |
7.09a |
0.038 |
<0.001 |
0.020 |
0.190 |
|
N concentration of cultivated substrate (g/kg) |
14.54c |
17.43a |
16.21b |
17.27a |
0.192 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 | |
|
Total N in cultivated substrate (g) |
101.1c |
124.3a |
110.4b |
121.2a |
1.350 |
<0.001 |
0.012 |
<0.001 | |
|
N retention rate during cultivation3(%) |
40.64c |
43.07b |
44.87a |
42.98b |
0.460 |
0.564 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 | |
|
Harvested mushroom |
Fruit body yield (kg DM) |
0.080a |
0.067b |
0.047c |
0.052c |
0.002 |
0.129 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
|
N concentration in fruit body (mg/kg) |
18.27 |
18.52 |
18.24 |
18.17 |
0.301 |
0.755 |
03542 |
0.600 | |
|
Total N in fruit body (g) |
1.463a |
1.247b |
0.852c |
0.948c |
0.049 |
0.231 |
<0.001 |
0.004 | |
|
N recycled rate4(%) |
5.88a |
4.31b |
3.46c |
3.33c |
0.189 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
0.001 | |
NC= no-antibiotic manure and corn straw, NW: no-antibiotic manure and wheat straw, AC= antibiotic manure and corn straw, AW= antibiotic manure and wheat straw, N retention rate= Total N in fermented substrate/Total N in starting substrate, N retention rate= Total N in cultivated substrate/Total N in fermented substrate, N recycled rate= Total N in fruit body of mushroom/ Total N in starting substrate.
表2. 基质发酵和蘑菇栽培过程中的关键酶活性
|
Index |
Stage |
Treatment1 |
SEM |
Pvalue | |||||
|
No-antibiotic |
Antibiotic | ||||||||
|
NC |
NW |
AC |
AW |
Straw |
Antibiotic |
Straw × Antibiotic | |||
|
Urease (U/g) |
End of feeding |
5770.3b |
5775.5b |
8556.4a |
8125.7a |
277.74 |
0.453 |
<0.001 |
0.442 |
|
End of fermentation |
3014.6b |
3911.0a |
2345.1c |
2173.2d |
24.30 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 | |
|
End of cultivation |
43.38b |
218.80a |
45.10b |
32.01c |
0.704 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 | |
|
Nitrate reductase (U/g) |
End of feeding |
7.43b |
7.25b |
13.61a |
13.63a |
0.147 |
0.611 |
<0.001 |
0.529 |
|
End of fermentation |
1.04b |
1.18a |
0.74c |
0.90d |
0.012 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
0.631 | |
|
End of cultivation |
38.75bc |
49.2b |
30.24c |
152.4a |
4.104 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 | |
|
Nitrite reductase (U/g) |
End of feeding |
15.77b |
15.79b |
15.94a |
15.95a |
0.078 |
0.731 |
0.002 |
0.890 |
|
End of fermentation |
14.20a |
10.49d |
11.22c |
13.02b |
0.018 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 | |
|
End of cultivation |
11.22a |
9.49b |
8.58c |
8.48d |
0.028 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 |
<0.001 | |
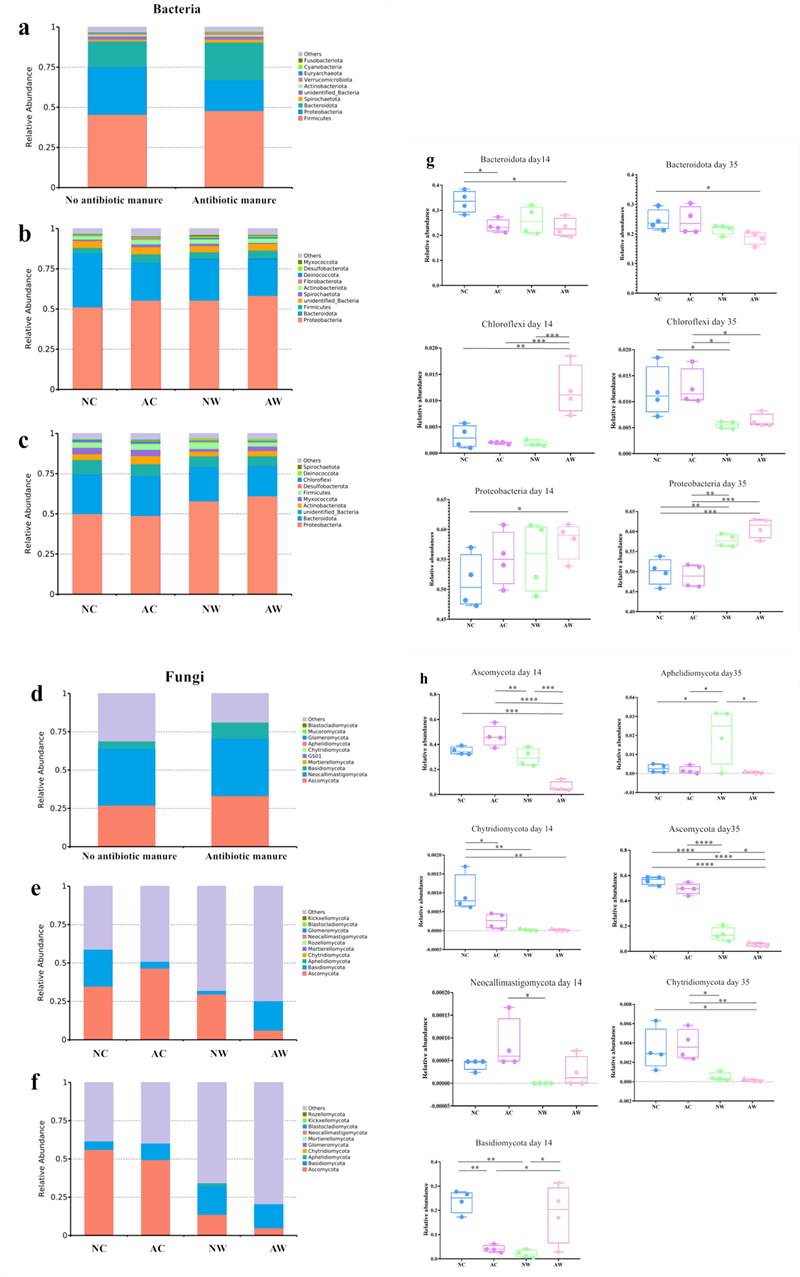
图1. 基质发酵第0天(a)、14天(b)、35天(c)基于 16S rDNA 测序的门水平相对丰度;堆肥第0天(d)、14天(e)、35 天(f)基于 ITS 测序的门水平相对丰度。
研究成果于近期发表在国际期刊Waste Management上,由王菲研究实习员(第一作者)和钟荣珍研究员(通讯作者)共同完成。该研究得到了中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDA28020400 ; XDA28080400 ; XDA23070503 );吉林省与中国科学院科技合作高技术产业化专项资金项目(2021SYHZ0033);吉林省科技发展计划项目(20200602016ZP )和中国科学院青年创新促进会优秀会员人才专项( Y201949 )的联合资助。
文章信息:Wang F., Fang Y., Wang L. X., Xiang H., Chen G. S., Chang X., Liu D., He X. M., Zhong R. Z.*2022. Effects of residual monensin in livestock manure on nitrogen transformation and microbial community during “crop straw feeding-substrate fermentation-mushroom cultivation” recycling system. Waste Management. 149. 333-344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.06.015.
附件下载:
 吉公网安备22017302000214号
吉公网安备22017302000214号